Understanding Ethylene (C2H4): The Essential Organic Compound
Ethylene (C2H4), a simple organic compound composed of two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms, holds significant importance in the fields of chemistry and agricultural science. With a molecular weight of 28.054, ethylene is characterized by a carbon-carbon double bond that distinguishes it from other hydrocarbons.
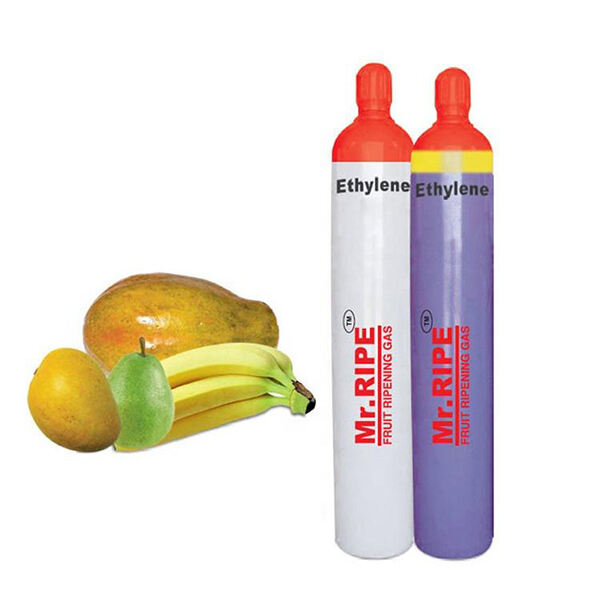

The Role of Ethylene in Nature
In nature, ethylene is not just an industrial chemical; it plays a crucial role within plant physiology. Ethylene is present in various tissues and organs of plants and is synthesized from methionine under oxygen-rich conditions. As a confirmed plant hormone, ethylene influences numerous physiological processes in plants, including:
- Fruit Ripening: Ethylene acts as a natural ripening agent, accelerating the process of maturation in fruits.
- Leaf Senescence: The compound promotes the aging process in plant leaves.
- Root Development: Ethylene induces adventitious roots and hair formation, enhancing nutrient absorption.
- Seed Dormancy Breakage: It assists in breaking dormancy in seeds and buds, initiating growth.
- Flower Induction and Gender Determination: Ethylene can suppress flowering in many plants, but it can also induce flowering in certain species such as pineapple. In dioecious plants, ethylene may change the direction of sexual differentiation during early flower development.
Ethylene: A Key Player in Industrial Chemistry
Beyond its natural significance, ethylene's industrial applications are extensive. As one of the most produced chemical products globally, the ethylene industry serves as a cornerstone of the petrochemical sector. Interestingly, ethylene products account for more than 75% of the petrochemical output, demonstrating its pivotal role in the economy.
Ethylene is the fundamental raw material for the production of various synthetic materials, including:
- Synthetic Fibers: Used in textiles and apparel.
- Synthetic Rubber: Indispensable in tire manufacturing and other rubber products.
- Plastics: Ethylene is integral in producing polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), widely used in packaging and construction.
- Ethanol Production: Ethylene serves as a precursor to synthetic ethanol (alcohol), widely utilized in beverages and industrial applications.
- Other Chemicals: Ethylene is also used in the production of chlorinated compounds like chloroethene (vinyl chloride), styrene, epoxy compounds, acetic acid, acetaldehyde, and explosives.
Economic Importance of Ethylene
The production of ethylene is often used as an indicator of a country's level of development in the petrochemical industry. Countries producing high quantities of ethylene signify a robust oil and chemical sector, which in turn contributes significantly to the national economy.
Conclusion
In summary, ethylene (C2H4) is not only a vital compound in the realm of organic chemistry but also serves various ecological and industrial purposes. Its role as a plant hormone and its extensive use in the production of synthetic materials underscore its significance. Understanding ethylene enhances our appreciation of both natural processes and technological advancements in the field of chemistry, paving the way for innovations in agriculture and manufacturing.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 BE
BE
 KA
KA
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MI
MI
 MR
MR
 MN
MN
 NE
NE
 UZ
UZ

